News
- Home
- Teleradiology Workflows Explained | From Scan to Report
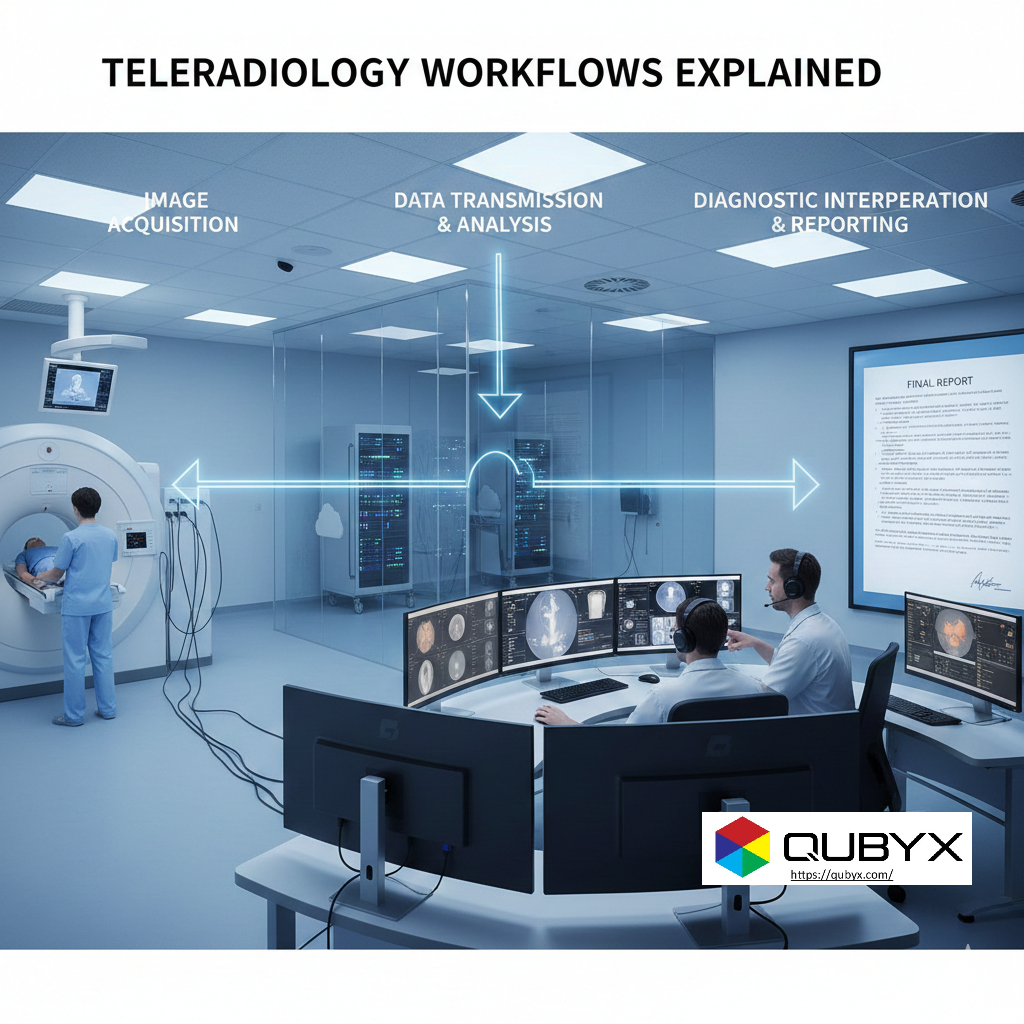
Teleradiology Workflows Explained | From Scan to Report
- January 6, 2026
- Shamsul
Teleradiology Workflows Explained—from Image Acquisition to Final Report
Teleradiology has become a foundational pillar of modern diagnostic healthcare. As imaging volumes rise and radiologist shortages persist, healthcare systems increasingly depend on teleradiology workflows to ensure continuity of care, rapid turnaround times, and diagnostic accuracy across geographies.
Understanding teleradiology workflows—from the moment an image is captured to the delivery of the final radiology report—is essential for hospital administrators, radiologists, IT leaders, and imaging service providers. This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step explanation of how teleradiology workflows function in real-world clinical environments.
1. What Are Teleradiology Workflows?
At their core, teleradiology workflows describe the end-to-end process that enables medical images to be:
-
Acquired at one location
-
Transmitted securely to a remote radiologist
-
Interpreted using diagnostic systems
-
Converted into a structured report
-
Delivered back to the referring clinician
Unlike traditional on-site radiology, teleradiology workflows rely heavily on digital infrastructure, interoperability standards, and quality controls to replicate—and often exceed—the reliability of in-house reading rooms.
2. Step One: Image Acquisition at the Source
Every teleradiology workflow begins with image acquisition. This occurs at hospitals, imaging centers, emergency departments, or mobile diagnostic units.
Key Characteristics of This Stage
-
Modalities include CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, and mammography
-
Images are captured in DICOM format
-
Patient demographics and exam metadata are embedded at creation
Accuracy at this stage is critical. Errors in patient data, imaging parameters, or modality calibration can propagate downstream, impacting the entire teleradiology workflow.
3. Step Two: Image Validation and Quality Check
Before images enter the broader teleradiology workflows, most systems apply automated or semi-automated checks:
-
Verification of patient identifiers
-
Completeness of image series
-
Basic image quality screening
-
Modality compliance validation
This step ensures that only diagnostically viable studies proceed, reducing rework and minimizing interpretation delays.
4. Step Three: Secure Image Transmission
Once validated, images are transmitted through secure networks—often cloud-based—to remote reading environments.
Core Transmission Requirements
-
Encrypted data transfer
-
Redundancy and failover mechanisms
-
Compliance with healthcare data regulations
-
High availability and low latency
Efficient transmission is a defining feature of modern teleradiology workflows, particularly for emergency and after-hours cases.
5. Step Four: PACS and RIS Integration
At the destination, images are ingested into a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) and coordinated through a Radiology Information System (RIS).
Why This Integration Matters
-
Enables worklist automation
-
Supports case prioritization
-
Tracks reporting status
-
Maintains audit trails
Seamless PACS–RIS integration allows teleradiology workflows to scale across thousands of studies without losing operational visibility.
6. Step Five: Worklist Management and Case Allocation
Advanced teleradiology workflows use intelligent worklist engines to assign cases based on:
-
Radiologist subspecialty
-
Licensure and credentialing
-
Time zone and availability
-
Urgency and clinical priority
This automated orchestration is one of the greatest efficiency advantages of teleradiology, enabling faster turnaround times compared to static, location-bound models.
7. Step Six: Diagnostic Image Interpretation
This is the clinical core of teleradiology workflows. Radiologists review images using diagnostic-grade displays and advanced viewing software.
Key Elements of Interpretation
-
Accurate grayscale and color rendering
-
Access to prior studies
-
Measurement and annotation tools
-
Hanging protocols optimized per modality
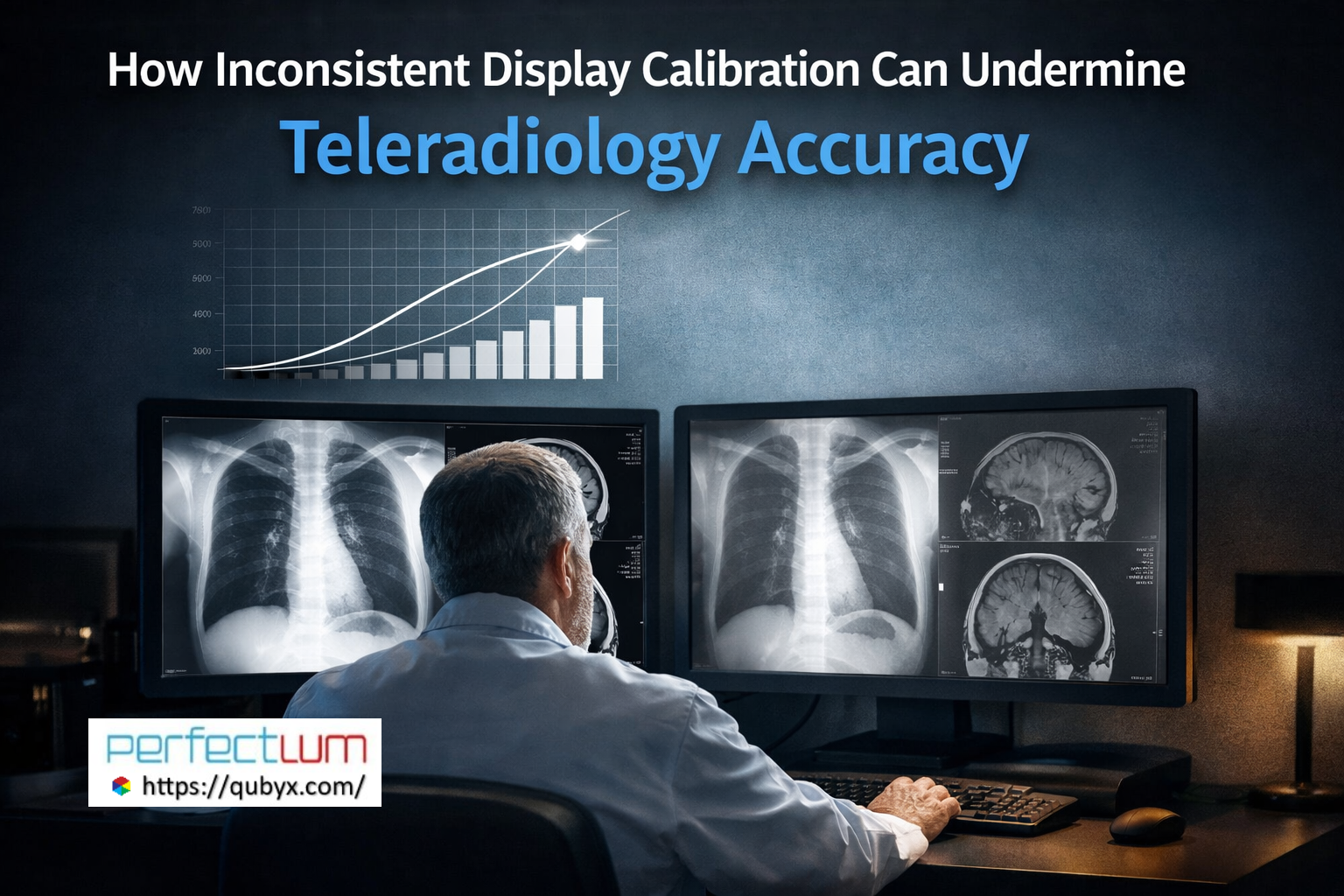
Any compromise in display quality or software performance can undermine the integrity of teleradiology workflows, making quality assurance at this stage essential.
8. Step Seven: Report Creation and Validation
After interpretation, findings are documented through structured or semi-structured reporting systems.
Reporting Features in Teleradiology Workflows
-
Voice recognition and dictation
-
Structured templates
-
Clinical decision support
-
Peer review triggers
Reports often undergo secondary validation—either automated or human—to ensure clarity, accuracy, and compliance.
9. Step Eight: Report Transmission and Clinical Delivery
Once finalized, reports are securely delivered back to the originating site or electronic health record (EHR).
Delivery Considerations
-
Immediate availability for critical findings
-
Alerting mechanisms for urgent cases
-
Integration with hospital information systems
This final stage completes the teleradiology workflow, enabling clinicians to act quickly on diagnostic insights.
10. Quality Assurance Across Teleradiology Workflows
High-performing teleradiology workflows incorporate continuous quality assurance, including:
-
Display calibration monitoring
-
Reader performance analytics
-
Turnaround time tracking
-
Compliance audits
Quality assurance is not a separate function—it is embedded throughout the entire teleradiology workflow lifecycle.
11. Compliance and Security in Teleradiology Workflows
Because teleradiology workflows operate across borders and jurisdictions, regulatory compliance is critical.
Key compliance pillars include:
-
Patient data privacy
-
Secure authentication and access control
-
Auditability and traceability
-
Jurisdictional licensing alignment
Robust governance frameworks ensure teleradiology workflows remain legally defensible and clinically trustworthy.
12. Why Optimized Teleradiology Workflows Matter
When designed correctly, teleradiology workflows deliver measurable benefits:
-
Faster report turnaround times
-
Expanded subspecialty access
-
Reduced radiologist burnout
-
Improved patient outcomes
-
Scalable diagnostic capacity
Conversely, poorly designed teleradiology workflows introduce risk, inefficiency, and diagnostic variability.
Frequently Asked Questions (People Also Ask)
Q1: What are teleradiology workflows?
Teleradiology workflows are the end-to-end processes that enable medical images to be acquired, transmitted, interpreted remotely, and reported back to clinicians securely and efficiently.
Q2: How do teleradiology differ from on-site radiology?
This workflows rely on digital transmission, remote worklists, and distributed reading environments, whereas on-site radiology depends on physically co-located systems and staff.
Q3: What technologies support this workflows?
Core technologies include imaging modalities, PACS, RIS, secure networks, diagnostic viewing software, reporting tools, and quality assurance systems.
Q4: It Safe safe and reliable?
Yes—when properly implemented, it can match or exceed the safety and reliability of traditional radiology through automation, redundancy, and continuous monitoring.
Q5: What is the biggest risk in workflows?
The most significant risks involve inadequate quality control—particularly display accuracy, data integrity, and compliance gaps—which can affect diagnostic confidence.
Final Thoughts
As healthcare systems continue to decentralize, teleradiology workflows will only grow in importance. From image acquisition to final report delivery, every stage must be optimized, monitored, and governed to ensure diagnostic excellence.
Organizations that invest in well-designed teleradiology workflows are not just improving operational efficiency—they are strengthening the very foundation of modern diagnostic care.
Start the conversation with our calibration experts today.
In a world where every Pixel accuracy matters, PerfectLum by QUBYX proves that innovation can deliver clinical precision without financial compromise. It’s not just calibration—it’s the democratization of diagnostic imaging.
To secure Medical Display Quality Assurance with precision while reducing the recurring costs of proprietary hardware, the answer is clear: transition to a Calibration Software platform with QUBYX OS Tools (Free) and PerfectLum today. Now, you easily pay less for Radiology.
Tags:
teleradiology workflows, teleradiology process, radiology workflow automation, image acquisition in teleradiology, PACS RIS integration, remote radiology reporting, teleradiology quality assurance, teleradiology compliance
Related Posts
- January 9, 2026
- News
End-to-End Image Integrity | The Key to Teleradiology Success
- January 8, 2026
- News
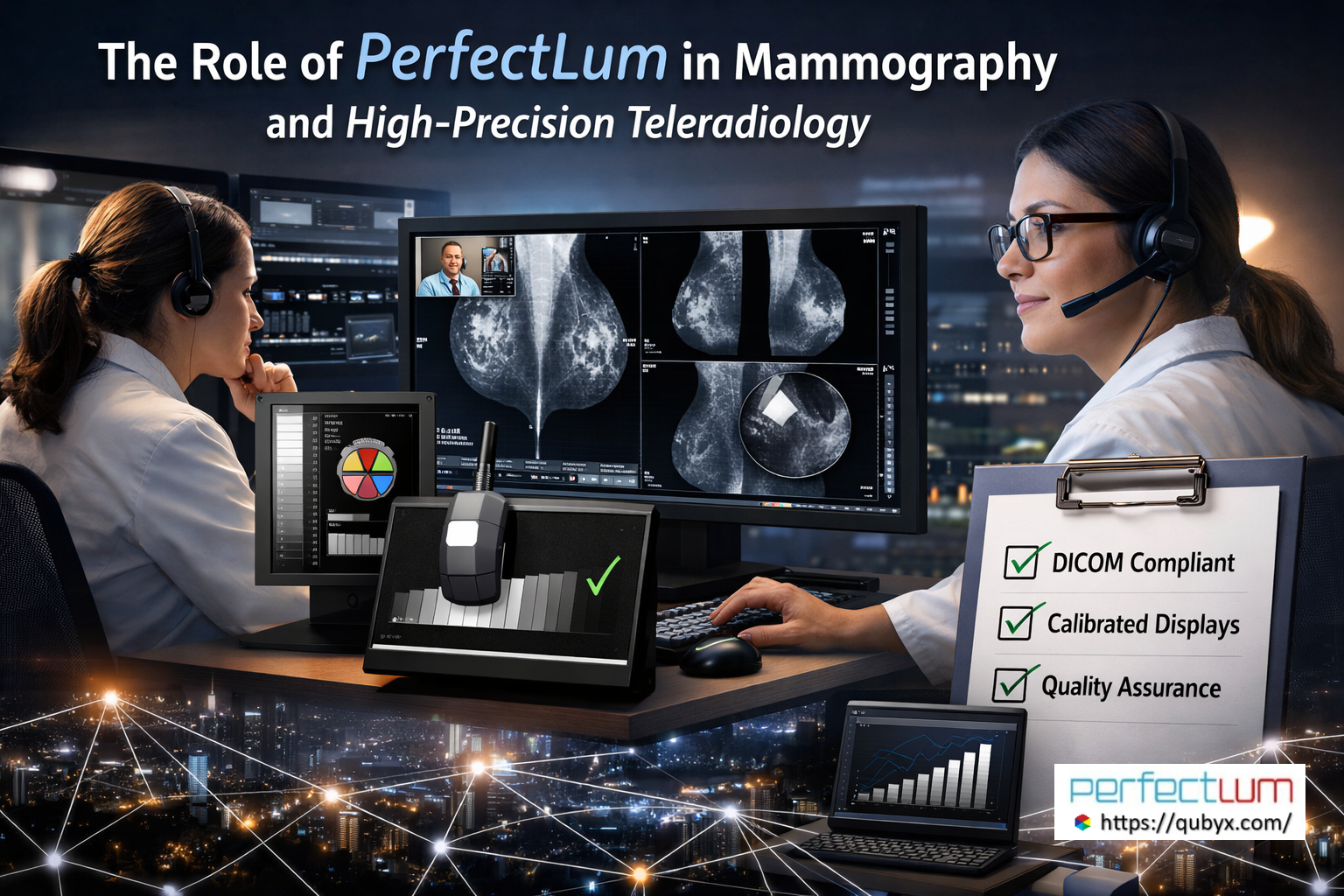
PerfectLum in Mammography & High-Precision Teleradiology Why Display Accuracy Is
- January 8, 2026
- News
Why PerfectLum Is Essential for Multi-Site Teleradiology Operations A